Hitting heifer liveweight targets
Early December marks a key transition for many dairy farmers, as weaned replacement heifers head off-farm to grazing.
In my last article, I covered factors affecting the marginal returns from growing maize on-farm.
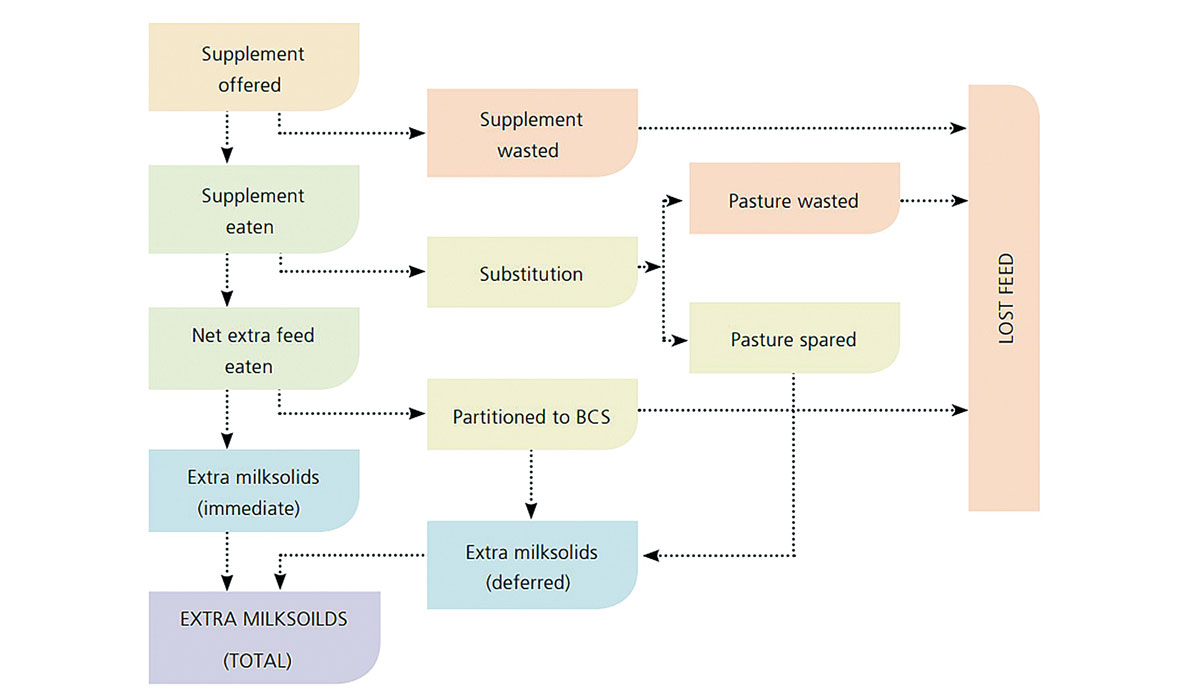
While yield and costs are often focal points, how maize silage is fed within a dairy system effects milk response and, ultimately, has a big impact on economic returns. During my dayto- day work, I’ve had the privilege of observing how top dairy farmers achieve milk responses as high as 100 grams of milksolids (MS) per kg of dry matter (DM) fed. These farmers pay attention to feed-out management and feeding accuracy to minimise wastage, they understand how substitution works, and they design their systems to maximise the utilisation of additional feed. Figure 1 below illustrates how feed can be partitioned within a system and shows why not all feed is converted into additional milk.
Minimising wastage
Wastage is an inevitable challenge when offering supplementary feeds to grazing cows. Losses occur at the stack (heating and spoilage) as well as during feeding out (feed left uneaten in the paddock or feed bin). The extent of this wastage depends on the management practices, feeding methods, and infrastructure in place. Top operators take specific measures to minimise these losses.
Precision feeding: Understanding the pasture supply curve and feed budgeting helps to ensure they have sufficient feed to maintain a consistent supply throughout the season. This helps prevent under or over feeding at any time during the season.
Silage quality: Highquality, well-preserved silage means that more of the energy is retained in the stack. Farmers using proven ensiling techniques, such good compaction, covering completely with tyres and applying inoculants, often see fewer losses and better overall feed quality.
Infrastructure: Investing in feed pads or troughs reduces feed wastage significantly. Feeding on a pad can keep wastage as low as 10%, even in challenging weather, while feeding directly in paddocks, especially in wet conditions, can increase wastage to as much as 40%. It can also create pasture damage which impacts pasture yields especially when ground conditions are wet.
Understanding substitution
Substitution occurs when cows reduce pasture intake in response to increasing supplementary feed. This effect can have both positive and negative impacts. On the downside, cows may leave good-quality pasture uneaten, leading to wasted drymatter and/or a loss in feed energy as pasture quality decreases. However, substitution can also create opportunities. For instance, using supplements to manipulate rotation length and achieve optimum pre and post grazing covers can lead to extra pasture grown or “saved,” contributing to a deferred milk response. Top farmers using maize silage leverage positive substitution while minimising negative effects:
Maintaining pasture grazing pressure: These farmers carefully manage animals and feed. They adjust stocking rates (typically higher), calving dates (early and/or split calving), and drying-off dates to achieve high cow days in milk each season. These strategic decisions also create larger pasture deficits that can be filled with maize silage while maintaining consistent grazing pressure and minimising substitution.
Strategic supplement type and timing: Timing and type of supplements influence substitution rates. For example, during high-substitution periods like during the peak of spring pasture growth, top operators often lean towards supplying concentrate feeds over forage feeds, as they create less substitution. However, typically these feeds are more expensive, so they are often fed for short periods and then replaced with typically cheaper forage-based feed.
 |
|---|
|
|
Adjusting seasonally: Substitution rates tend to be highest in spring and lower in the summer and autumn. Having stored maize silage to feed as part of the diet in summer and autumn helps to achieve pasture and BCS targets that contribute to achieving a deferred milk response.
Optimising feed partitioning for milk production.
Ensuring that supplementary feed is converted efficiently into milk rather than maintenance is another priority for top operators. Achieving high production per cow and minimising body condition fluctuations throughout the season ensures the energy from supplements contributes more effectively to milk production rather than maintenance and replenishing body reserves.
Maintaining consistent body condition score: Farmers who meet body condition score (BCS) targets before calving and maintain them through lactation limit the energy losses associated with gaining and mobilising BCS.
For example, a lactating cow requires 50 MJME to store one kg liveweight (LWT); however, mobilising one kg LWT only supplies the cow with 37 MJME.
Leveraging high genetic merit cows: Highgenetic merit cows tend to prioritise milk production over building body reserves. This makes them more efficient at converting supplementary feed into milk.
If you would like to understand how to get more production from the supplements you are feeding, feel free to give me or my colleague Matt Dalley a call. Our contact details can be found at pioneer.co.nz.
Wade Bell is Genetic Technologies farm systems manager. Contact him at This email address is being protected from spambots. You need JavaScript enabled to view it.
New Zealand farming is riding a high, with strong prices, full feed covers and improving confidence lining up at the same time.
Manawatu Mayor Michael Ford says the district sees itself as the agribusiness capital of the lower North Island.
Beef + Lamb New Zealand (B+LNZ) is looking forward to connecting with farmers, rural professionals and community members at this year's Central District Field Days.
Labour Party Leader Chris Hipkins has announced a reshuffle of the party's caucus portfolios.
Agriculture Minister Todd McClay says a series of rural resilienced set to be rolled out next week will help farmers and growers better prepared for adverse weather events.
Stefan and Rachel Grobecker were named Share Farmers of the Year at last night's 2026 Bay of Plenty Dairy Industry Awards dinner.
OPINION: Expect the Indian free trade deal to feature strongly in the election campaign.
OPINION: One of the world's largest ice cream makers, Nestlé, is going cold on the viability of making the dessert.