Hitting heifer liveweight targets
Early December marks a key transition for many dairy farmers, as weaned replacement heifers head off-farm to grazing.
 In well-managed systems, silage wastage may be as low as 10%, but poor feed management can push wastage rates as high as 50%.
In well-managed systems, silage wastage may be as low as 10%, but poor feed management can push wastage rates as high as 50%.
Much has been discussed in recent seasons about the rising costs of production on dairy farms, and rightfully so.
Although we’ve seen input costs flatten out over the past six months, prices have risen by 24% since early 2021. This has led to all areas of farm businesses being scrutinised to ensure they still deliver a positive return in this higher-cost environment, including growing maize on-farm.
It’s also important to balance rising costs with changes in milk price, which has increased by similar levels over the same period. So, while cost control remains critical, we also need to remain focused on the margin generated from any expense incurred within the business. So, in the context of growing maize on-farm, what are the critical elements to ensure a positive margin is achieved?
1. Input Costs
Growing costs, including seed, cultivation, spraying, fertiliser, labour, and machinery are important. At Pioneer, we review these annually and publish them in our catalogue and on our website. However, we encourage farmers to calculate their own costs based on their local conditions.
For the 2024/25 season, per hectare growing and harvesting costs were calculated at $4,035 to $5,250 for high and typical fertility environments, respectively. High fertility environments including paddocks with a history of effluent application, may not require any additional fertiliser hence the lower growing costs.
When determining the real cost of growing maize on farm farmers must also consider the opportunity cost of pasture forgone and any saved costs e.g. not harvesting surplus pasture. By dedicating paddocks to maize silage, farmers forgo the ability to harvest maybe 6-8 t DM/ha of pasture during that period. So, the net cost to cost to grow maize on farm is often between 20-30c per kgDM, which is still favourable relative to imported feed options.
2. Yield Potential
Maize’s yield potential is one of its biggest advantages. Every additional tonne of dry matter harvested can reduce the overall feed cost by approximately 1c per kg DM. Recently, I listened to a colleague, Dr Rowland Tsimba, present that maize has the potential to yield as much as 40t DM/ha. While this may raise eyebrows, the key factors that drive yield potential are what farmers should focus on. These are:
3. Minimising Wastage
In well-managed systems, silage wastage may be as low as 10%, but poor feed management can push wastage rates as high as 50%. When wastage is high, the effective cost of maize silage increases significantly, eroding the potential economic advantage.
For example, a 5% increase in feed wastage can add 1–2c per kg DM to the total cost of feed. Therefore, reducing wastage through proper storage, handling, and feeding systems is essential for maximising the marginal return from maize. Key management practices that help minimise wastage include:
4. Response to Supplementary Feed
The economic return from feeding maize silage depends largely on how effectively cows convert the extra feed into milk or body condition gain. The milk response, measured in grams of milk solids (MS) per kg DM fed, varies depending on a number of factors including wastage, substitution, feed quality, timing of feeding and cow health.
Research shows that milk responses to supplementary feed typically range from 0 to >100g MS per kg DM. We know that under ideal conditions the response to maize silage can be even higher. Feeding maize silage to achieve the highest milk response possible is critical to achieving a positive margin. Key factors that improve milk response include:
5. Bringing It All Together
 |
|---|
|
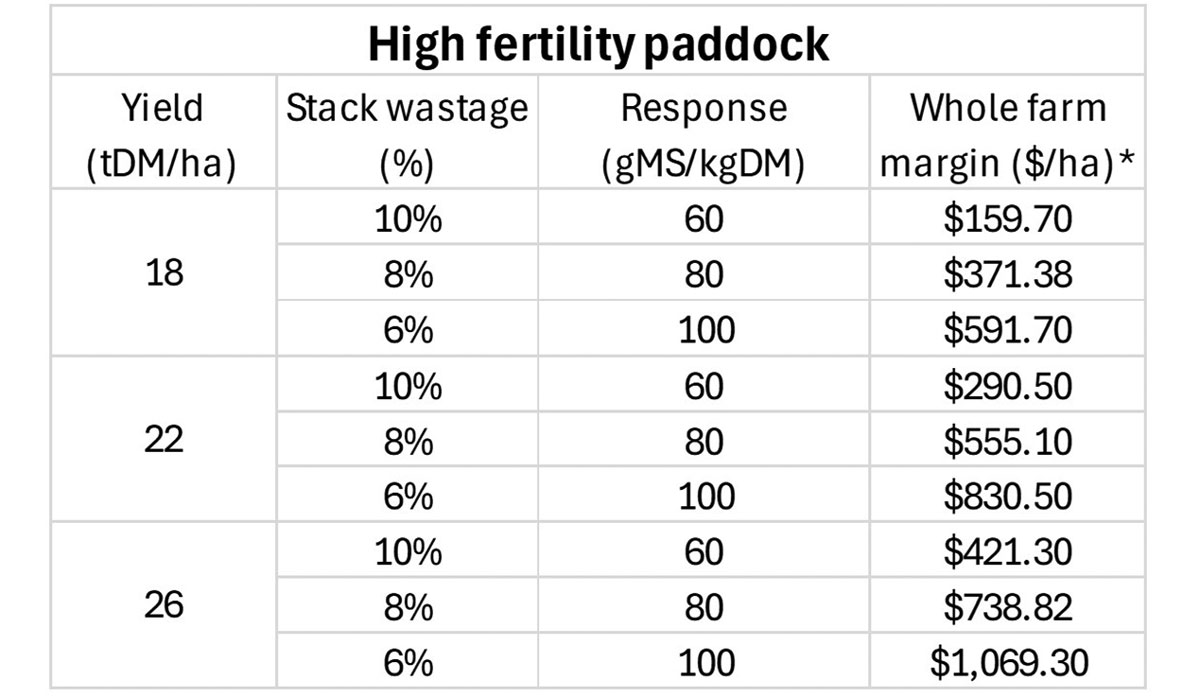
Table 1: Marginal returns from growing maize silage on a high fertility paddock and managing the feed well. |
cost environment, when done well, growing maize silage on-farm is still an effective way to reduce the cost of supplementary feed. Beyond cost, factors like yield, feed wastage and milk response should all be considered when assessing whether growing maize on farm is right. Top operators achieve high maize yields, minimise waste and efficiently convert the additional feed supply into milk to maximise profit margin (Table 1).
*Whole farm margin assumes maize grown on 10% of the farm area.
Wade Bell is Genetic Technologies farm systems manager. Contact him at This email address is being protected from spambots. You need JavaScript enabled to view it.
The Meat Industry Association of New Zealand (MIA) today announced that Chief Executive Officer Sirma Karapeeva has resigned from the role.
The winners of the 2026 Hawke’s Bay/Wairarapa Dairy Industry Awards were announced at the annual awards dinner held at Copthorne Solway Park in Masterton on Thursday evening.
Environment Southland is welcoming this week’s decision by the Environmental Protection Authority (EPA) to approve the release of Blaptea elguetai, a leaf‑feeding beetle that will help control the highly invasive Chilean flame creeper.
This March, the potato industry is proudly celebrating International Women’s Day on 8 March alongside the International Year of the Woman Farmer, recognising the vital role women play across every part of the sector — from paddocks and packhouses to research, leadership, and innovation.
Fruit trader Seeka posted a record profit and returns to shareholders in 2025.
Recent weather events in the Bay of Plenty, Gisborne/Tairawhiti, and Canterbury have been declared a medium-scale adverse event.
OPINION: Staying with politics, with less than nine months to go before the general elections, there’s confusion in the Labour…
OPINION: Winston Peters' tirade against the free trade deal stitched with India may not be all political posturing by the…