Green no more?
OPINION: Your old mate has long dismissed the Greens as wooden bicycle enthusiasts with their heads in the clouds, but it looks like the ‘new Greens’ may actually be hard-nosed pragmatists when it comes to following voters.
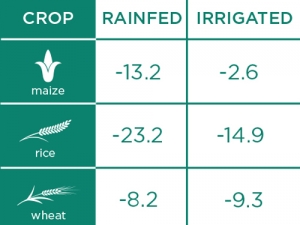 Effect of climate change on average maize, rice and wheat yields in 2050: Based on process-based models (DSSAT) between 2010 and 2050 (%). Source: IFPRI study
Effect of climate change on average maize, rice and wheat yields in 2050: Based on process-based models (DSSAT) between 2010 and 2050 (%). Source: IFPRI study
This year will likely be the hottest on record, according to the World Meteorological Organisation.
Depending on whether you are planning a beach holiday, or trying to keep your grass green, it could be a mixed blessing.
As temperatures continue to rise and extreme weather events such as droughts and floods become more frequent, worldwide farmers face more unpredictable and difficult growing conditions. Now, more than ever, global farmers need plant science technology to help combat climate change.
According to the International Food Policy Research Institute (IFPRI) rice, wheat and maize yields will fall significantly over the next 50 years without the aid of technology including crop protection and biotech traits to tackle climate change (see table).
Drastically reduced crop yields could have a devastating impact on global food security and that's where the plant science industry can help. Here are four technologies that are assisting farmers in many countries mitigate and adapt to climate change:
Heat-Tolerant Traits: The University of Florida has developed heat-tolerant biotech traits that showed yield increases of 38% in wheat, 23% in rice and 68% in maize grown in extreme and unexpected hot conditions.
Drought-Tolerance: For example the Water-Efficient Maize for Africa project is developing biotech traits that maintain and double maize yields in drought conditions.
Crop Protection Products: Climate change is pushing pests and diseases into new geographic areas. Crop protection products help farmers increase their yields despite the evolving threat and unanticipated changes in pest populations.
Nitrogen-Use Efficiency (NUE): Nitrogen fertiliser run-off can find its way into surrounding land and water. NUE traits will enable farmers to apply less nitrogen fertiliser without sacrificing yields.
While farmers worldwide will be challenged with climate change, smallholder farmers in developing countries could be hit the hardest – according to Agriculture for Impact, hunger and child malnutrition in Africa could increase by as much as 20% by 2050 as a result of climate change.
If the global community is to meet the United Nations' ambitious goal to end world hunger by 2030, while also facing up to the challenge of climate change, it will need these plant science tools at its disposal.
· Mark Ross is chief executive of Agcarm, New Zealand's industry association for companies which manufacture and distribute crop protection and animal health products.
Global trade has been thrown into another bout of uncertainty following the overnight ruling by US Supreme Court, striking down President Donald Trump's decision to impose additional tariffs on trading partners.
Controls on the movement of fruit and vegetables in the Auckland suburb of Mt Roskill have been lifted.
Fonterra farmer shareholders and unit holders are in line for another payment in April.
Farmers are being encouraged to take a closer look at the refrigerants running inside their on-farm systems, as international and domestic pressure continues to build on high global warming potential (GWP) 400-series refrigerants.
As expected, Fonterra has lifted its 2025-26 forecast farmgate milk price mid-point to $9.50/kgMS.
Bovonic says a return on investment study has found its automated mastitis detection technology, QuadSense, is delivering financial, labour, and animal-health benefits on New Zealand dairy farms worth an estimated $29,547 per season.

OPINION: Here w go: the election date is set for November 7 and the politicians are out of the gate…
OPINION: ECan data was released a few days ago showing Canterbury farmers have made “giant strides on environmental performance”.